Attachment styles and their association with aggression, hostility
4.7 (182) · $ 17.50 · In stock
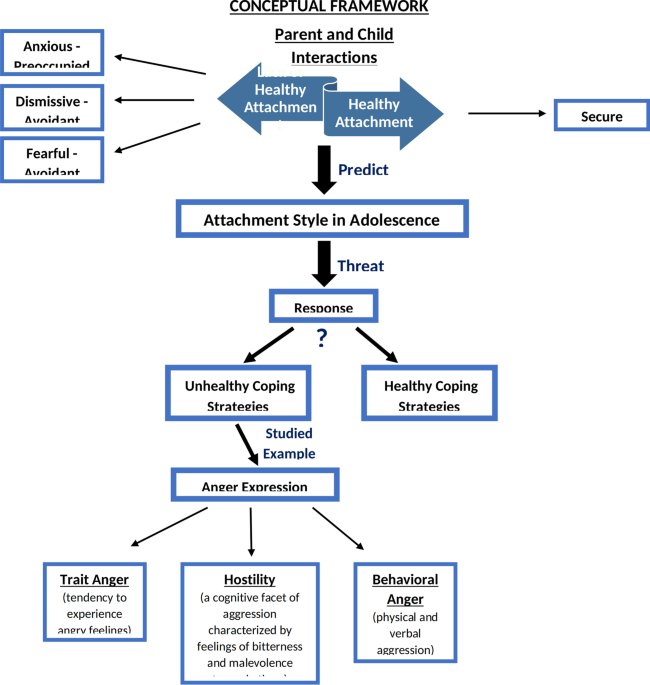
Background The idea that attachment styles can affect the level of anger in an individual educes a reason why people develop anger issues and behavioral problems in adolescence that escalate into adulthood. Lebanon suffers from a shortage of data pertaining to insecure attachment styles and the affective and cognitive aspects of anger and behavioral anger expression among the Lebanese youth population. This study aimed to investigate the association between attachment dimensions and anger expression (trait anger, hostility, physical aggression, and verbal aggression) among a sample of Lebanese adolescent participants. Methods This cross-sectional study was performed between January and May 2019 among 1810 Lebanese high-school students aged 12–18 and used two validated measures, the Adolescent-Relationship Questionnaire (A-RQ) and The Buss-Perry Aggression Questionnaire (BPAQ). The A-RQ assessed attachment behaviors, while the BPAQ evaluated aggression. Results Higher fearful and dismissing attachment styles, and higher physical activity index were significantly associated with higher physical and verbal aggression. A higher fearful attachment style was significantly associated with more anger. A higher secure attachment style was significantly associated with less anger. Higher preoccupied and dismissing attachment styles were significantly associated with higher hostility. Conclusion Our findings revealed a significant relationship between both insecure attachment dimensions and the tripartite model of anger expression. This study adds to the anger literature by providing a more informed understanding of how variations in anger expression are linked to the processing of interpersonal interactions, which are the hidden facets of attachment systems.

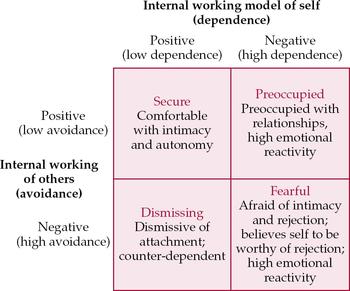
Dismissive-Avoidant Attachment

Anxious attachment style usually develops as a result of a parent, losing interest letra

Anxious attachment style usually develops as a result of a parent, losing interest letra

Attachment Styles and How They Affect Adult Relationships

Insecure attachment is significant predictor of anger expression among youth

Sample Characteristics of Homeless, Doubled-Up, and Housed Low-Income

Attachment styles predict personality traits according to a pilot

College hostility and risk: continuous and categorical models adjusted

Flow diagram for participants allocation

PDF) Agressivity in Adolescence and its Connection to Attachment

Mean values of the aggression scores according to the secure attachment
Attachment theory in adult psychiatry. Part 1: Conceptualisations

Hostility in college by patterns of change from college to midlife

College hostility and risk: continuous and categorical models adjusted