Physics Describing Motion. - ppt video online download
4.6 (611) · $ 19.50 · In stock

Aristotle BC One of the first to study motion Stated there were two kinds of motion Natural Motion Violent Motion
Physics Describing Motion.
Stated there were two kinds of motion. Natural Motion. Violent Motion.
the combination of the 4 elements: Objects wanted to get to natural place Ex: Smoke rises to be with air; Rocks fall to be with Earth. Straight up and Down (on Earth) Circular (in space) Believed different rules applied to the heavens, which were made of quintessence (perfect unchanging substance)
Ex: Person pushing a cart. Wind blowing a ship. EXTERNAL CAUSE, not due to nature of object.
Showed heavy and light objects fall at same rate. Forces are not needed to keep objects in motion. Inertia: Tendency of objects to resist change in motion. Objects at rest tend to stay at rest, Objects in motion tend to stay in motion until another force acts on it. Tested his ideas through experimentation. End of philosophizing about ideas. Beginning of modern science.
Amount of Inertia (resist in change of motion) depends on amount of mass. Mass: Amount of matter in an object; measured in kilograms (kg) DIFFERENT THAN WEIGHT! Weight: Force on an object due to gravity. Weight and mass are directly proportional. Double the Mass, Double the Weight! Which bucket would be harder to push WHY
1kg = 2.2 pounds (lb) 9.8N was rounded to 10.
What has more mass: 1kg rocks or 1 kg feathers Which liquid is the most dense Which solid is the most dense What has more weight: 1kg rocks or 1 kg feathers Which liquid is the least dense What is more dense: 1kg rocks or 1 kg feathers Which solid is the least dense
Vector Quantities: Forces shown by arrows. Have both magnitude (how much) and direction (which way)
Tension = Stretching Force. Is this diagram in equilibrium
Support Force. The force that supports an object against gravity – often called normal force. If the Normal Force is equal to the Weight, is the object in equilibrium If the Normal Force is less than the Weight, what happens
Equilibrium = state of no change. An object moving at a constant speed in a straight line is in equilibrium. Friction: Force that occurs opposite of motion when objects are in contact.
ALWAYS acts opposite the direction of movement. Ex: Air resistance: Force of friction acting on an object as it moves through the air.
Ex: Ridges in fingers allow you to grab things. When your hands are wet, water fills the ridges, you can’t hold on to things as well. Shooting Stars. Meteors are heated to the point of burning when entering our atmosphere due to hitting gas molecules. Earthquakes. Occur when the friction that is holding rock slabs together is overcome and plates slide past each other.
Triangle Method (always head to tail)
Vector Practice Free-Body Diagram: A sketch showing only the forces on the selected particle.
Units: km/hr; mi/hr; cm/min; km/day. Preferred unit: m/s. Instantaneous Speed: Speed at a given instant. Ex: Speedometer. Average Speed: averages all of the instantaneous speeds. Velocity: Speed AND Direction. Ex: 60mi/hr North; 30km/hr West. Is it possible to have constant speed but NOT constant velocity
Motion is Relative When we discuss speed or velocity, we mean RELATIVE to something else
Relative to bus vyou = +3m/s.
vyou, relative to street=11m/s.
Relative to street vyou = -3m/s.
vyou, relative to street= 5m/s.
Magnitude (speeding up OR slowing down) Direction. Units: m/s2. Ex: Gravity = 9.8m/s2.

PPT - Chapter 2 Describing Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free

PPT - Describing Motion PowerPoint Presentation, free download

541 powerpoint

Describing Motion and Related Concepts - Science Class 9 PDF Download

Describing Motion 2.1 Motion - ppt video online download
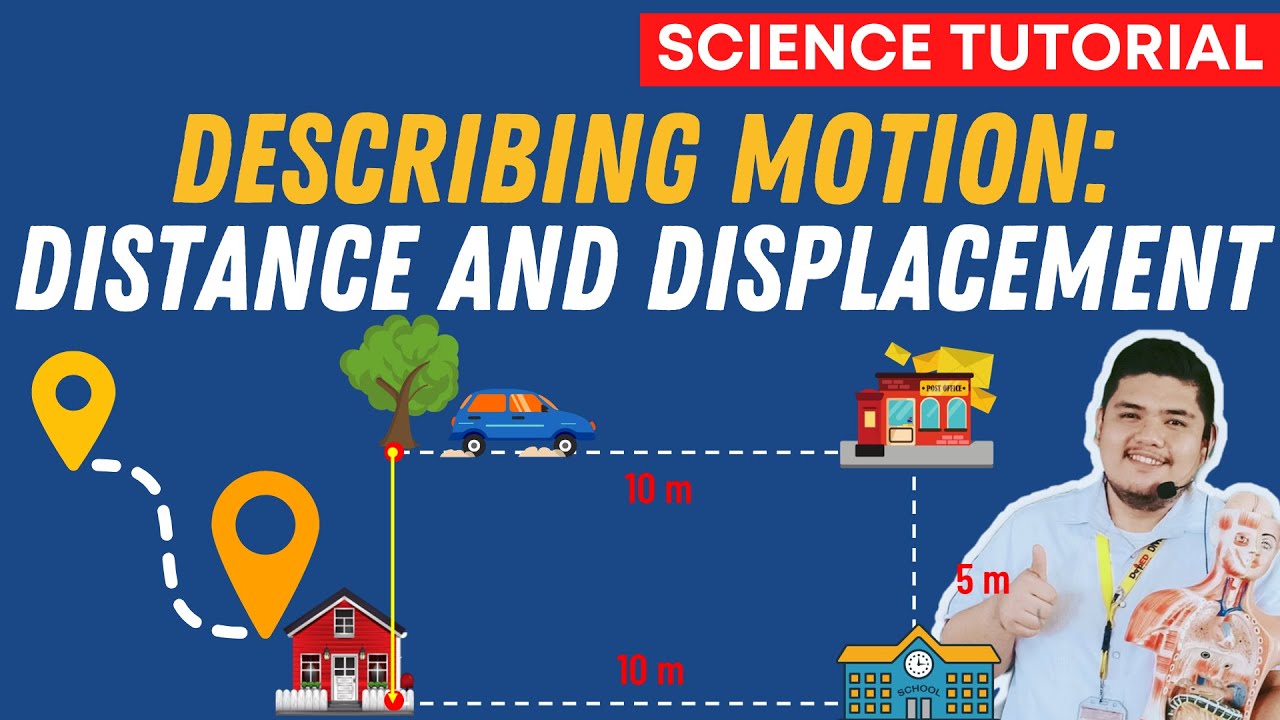
DESCRIBING MOTION: DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT

Chapter 3 Describing Motion. - ppt video online download

What Is Motion - Motion Definition, Types of Motion, Examples

Describing Motion 2.1 Motion - ppt video online download

Describing Motion

Thermodynamics An Engineering Approach Yunus A. Çengel - ppt video

DESCRIBING MOTION: DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT
This PowerPoint will introduce students to the basics of motion: speed (average and instantaneous), velocity, acceleration, and vectors. There are

Describing Motion PowerPoint (for Physical Science)

Digital Care Horizon: A Framework for Extending Health Care







