SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes inflammatory cytokine activation
5 (198) · $ 34.00 · In stock
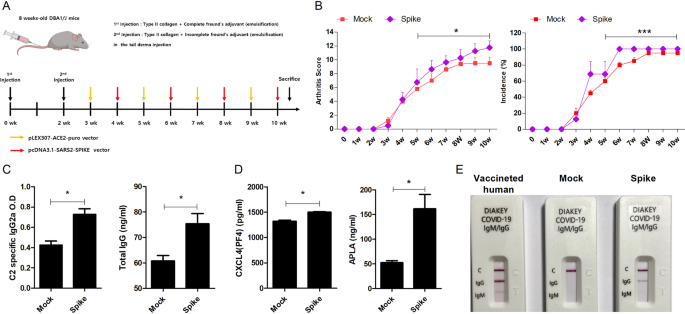
Background Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) induces inflammation, autoantibody production, and thrombosis, which are common symptoms of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, the effect of COVID-19 on autoimmune disease is not yet fully understood. Methods This study was performed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on the development and progression of RA using a collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) animal model. Human fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) were transduced with lentivirus carrying the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein gene in vitro, and the levels of inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were measured. For in vivo experiments, CIA mice were injected with the gene encoding SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and disease severity, levels of autoantibodies, thrombotic factors, and inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were assessed. In the in vitro experiments, the levels of inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression were significantly increased by overexpression of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in human FLS. Results The incidence and severity of RA in CIA mice were slightly increased by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in vivo. In addition, the levels of autoantibodies and thrombotic factors, such as anti-CXC chemokine ligand 4 (CXCL4, also called PF4) antibodies and anti-phospholipid antibodies were significantly increased by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Furthermore, tissue destruction and inflammatory cytokine level in joint tissue were markedly increased in CIA mice by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Conclusions The results of the present study suggested that COVID-19 accelerates the development and progression of RA by increasing inflammation, autoantibody production, and thrombosis. Video Abstract

SARS-CoV-2 drives NLRP3 inflammasome activation in human microglia through spike-ACE2 receptor interaction
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein promotes IL-6 trans-signaling by activation of angiotensin II receptor signaling in epithelial cells

CXCL4/PF4 ELISA DY595 from R&D Systems, a Bio-Techne Brand
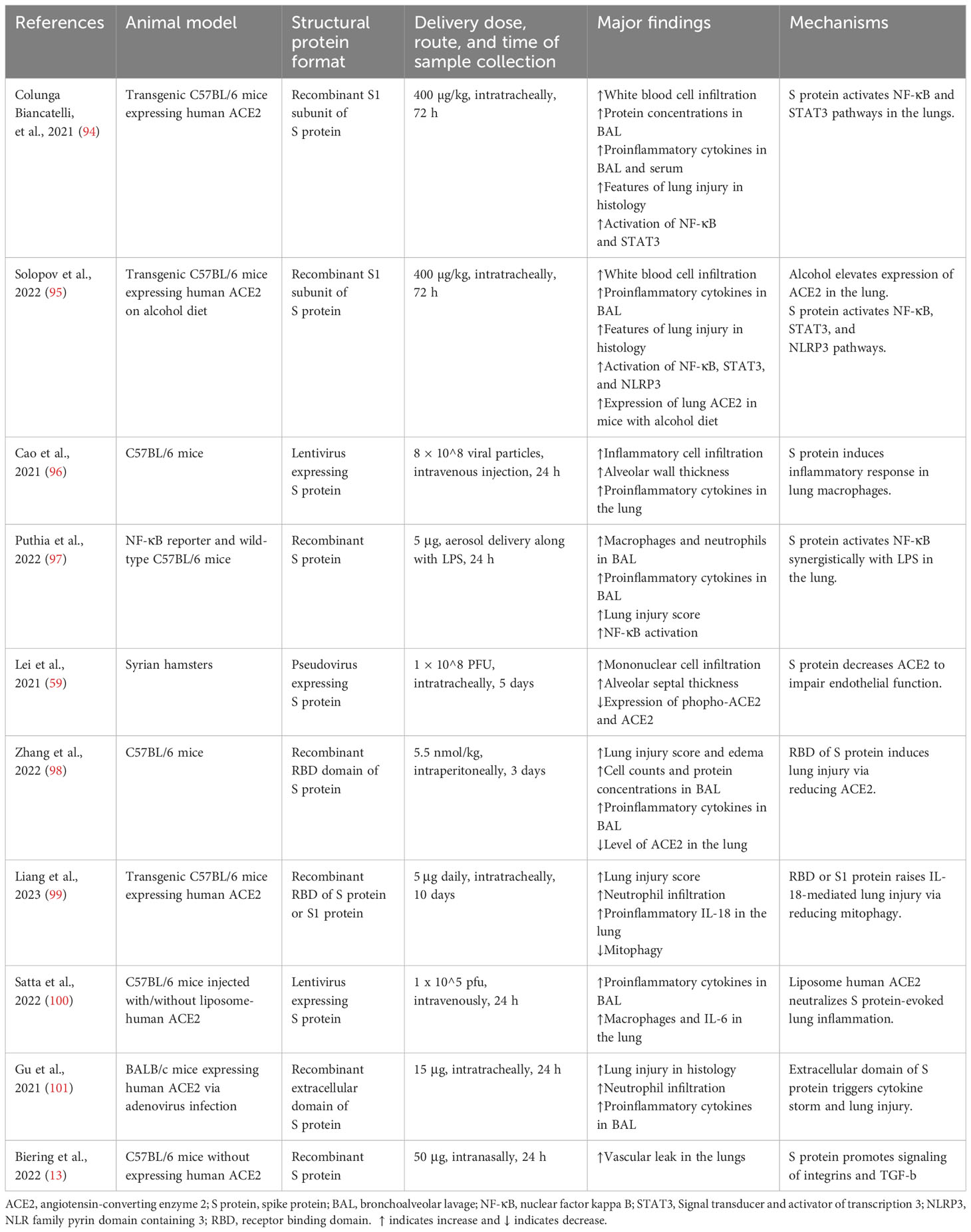
Frontiers Multifaceted role of SARS-CoV-2 structural proteins in
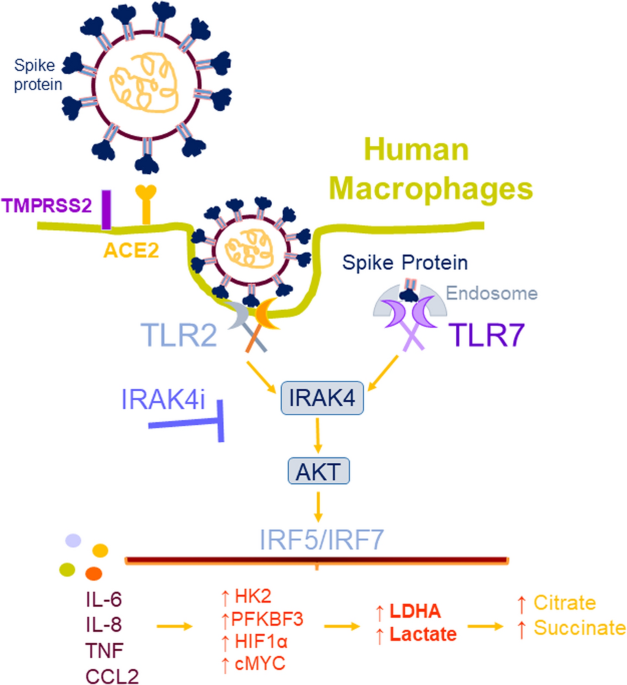
Inhibition of IRAK4 dysregulates SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced macrophage inflammatory and glycolytic reprogramming

STING activation leads to the inhibition of the mTORC1 pathway. (A

More than a key—the pathological roles of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in COVID-19 related cardiac injury - ScienceDirect
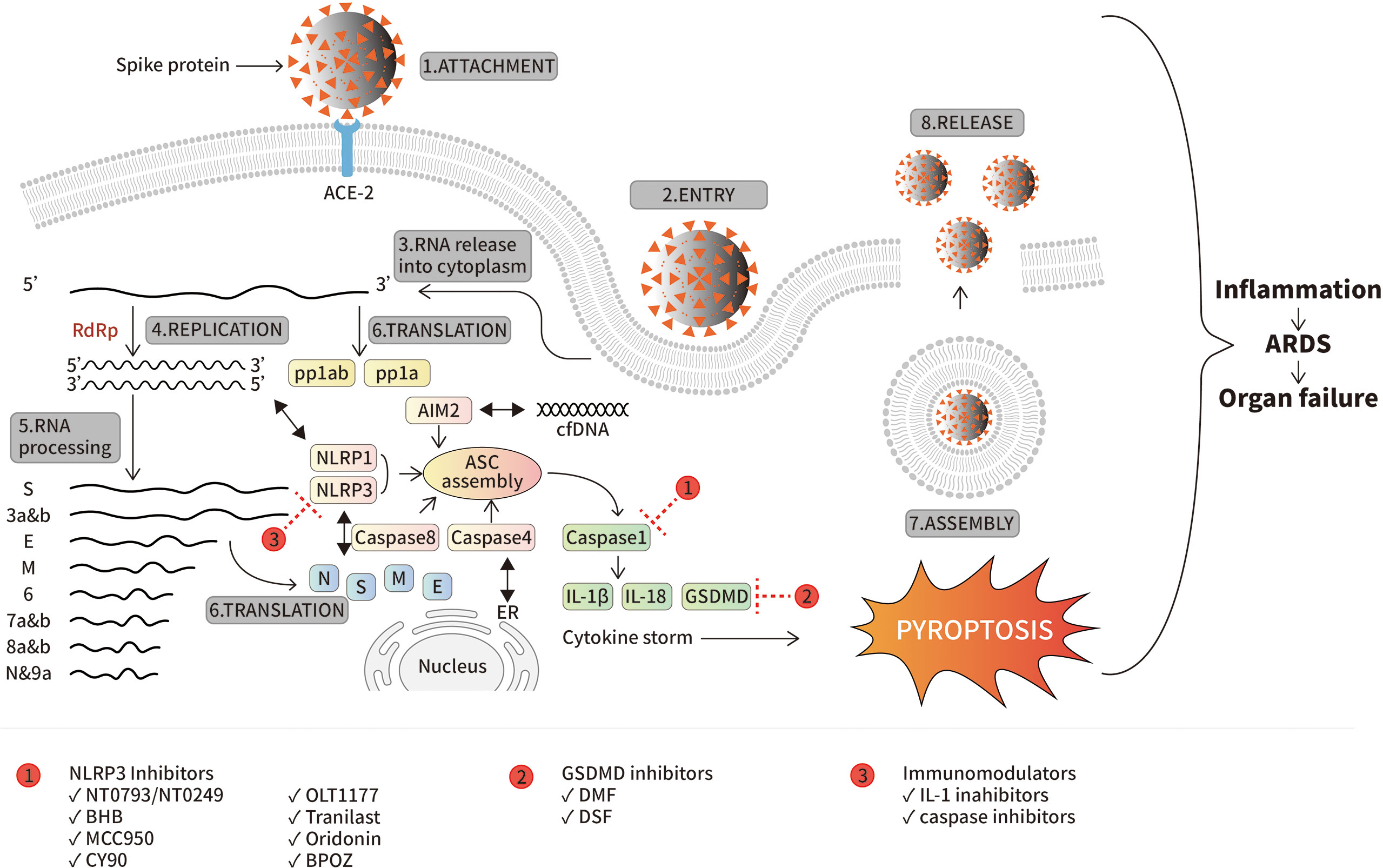
Frontiers Inflammasomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection and development of their corresponding inhibitors
![PDF] Immunotherapy of Autoimmune Diseases with Nonantibiotic](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/d85f3535b3ad71c851570a6dca15a0ad88d72851/4-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Immunotherapy of Autoimmune Diseases with Nonantibiotic

Mi-LA CHO, Professor (Associate), PhD
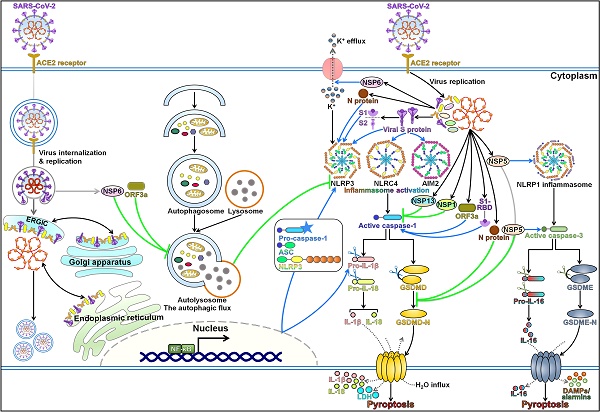
Pyroptotic cell death in SARS-CoV-2 infection: revealing its roles during the immunopathogenesis of COVID-19

Cytokines and microRNAs in SARS-CoV-2: What do we know? - ScienceDirect