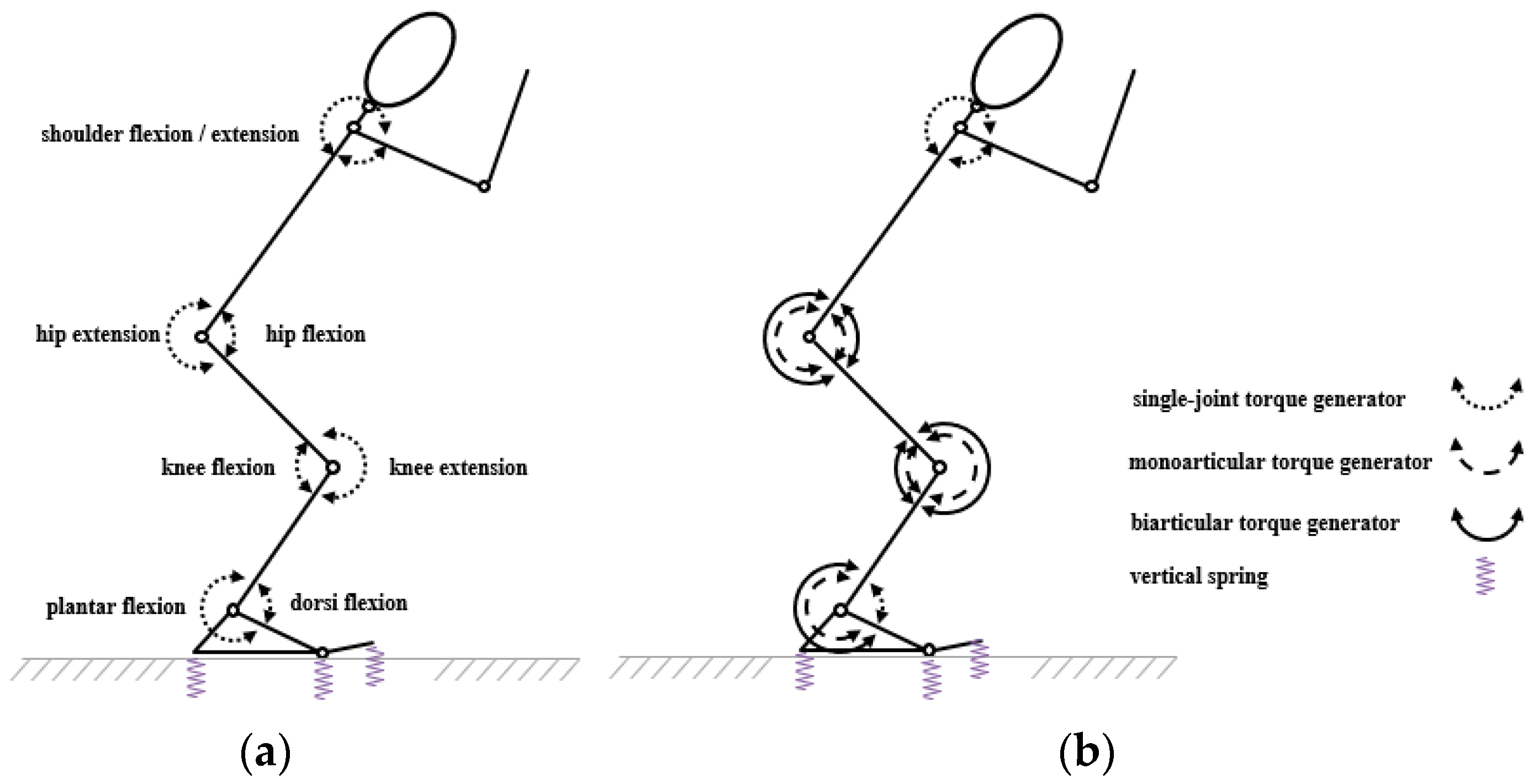
A powered simple walking model explains the decline in propulsive force and hip flexion torque compensation in human gait
4.9 (229) · $ 8.99 · In stock

Applied Sciences, Free Full-Text

A powered simple walking model explains the decline in propulsive force and hip flexion torque compensation in human gait

The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves for

Investigation of the relationship between steps required to stop and propulsive force using simple walking models - ScienceDirect

教員紹介

The Age-Associated Reduction in Propulsive Power Generation in Walking

Locomotion Laboratory

Research articles Scientific Reports

The reference limit cycle (red) and the actual solution (blue) for all

Hip joint power during walking and running. In the shaded interval

Relationship between v_N (N = 0, 1, 2, 3, 4) and the change in speed of

How Crouch Gait Can Dynamically Induce Stiff-Knee Gait

Altering Compliance of a Load Carriage Device in the Medial
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(740x153:742x155)/Tyra-excited-to-turn-50-1-112723-63c1843d78294e11996e266e3d787b7f.jpg)






